Components of Speech Language and Communication: An intentional, active two-way message exchange is communication. Humans converse with one another for a variety of reasons, including amusement. We see and take part in a range of communicative engagements every day. It maintains our relationships with one another. We all exchange or receive information during the day.
A group of people’s shared system of symbols is their language.
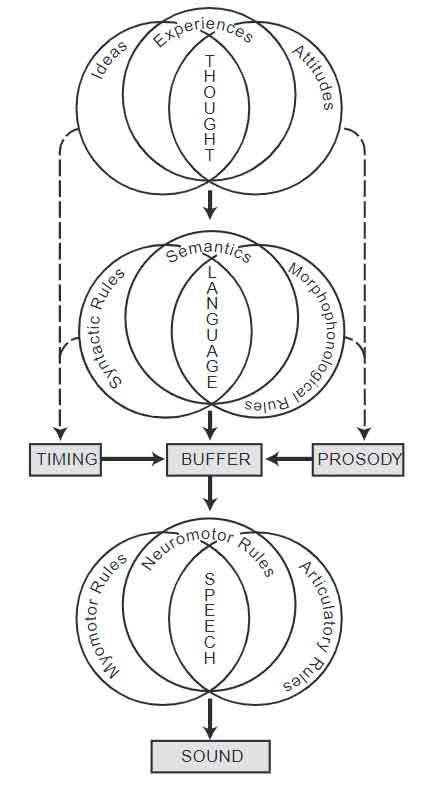
The primary means of communication is language, which effectively serves the same purposes as communication.
The most effective and popular way of language expression is speech. The most prevalent verbal codes in speech are spoken words. Specific word combinations are used to communicate meaning. Speech is produced by the tongue, jaw, lips, and other speech mechanism structures working in intricate cooperation with the neurological system.
SPEECH AND ITS COMPONENTS
Speech is a verbal form of communication that involves the production of sounds to convey meaningful messages. It is a complex process that includes the coordination of various components of the vocal tract, such as the lungs, vocal cords, tongue, lips, and jaw. Through speech, individuals articulate sounds and combine them to form words, sentences, and conversations.
Components of Speech
- Phonetics: Phonetics deals with the physical production, perception, and classification of speech sounds (phonemes). It focuses on studying the properties and characteristics of individual sounds, including their articulation, acoustic properties, and auditory perception.
- Phonology: Phonology explores the organization and patterns of sounds in a particular language or languages. It examines how phonemes combine to form meaningful units (morphemes) and how these units are structured within words and sentences.
- Articulation: Articulation refers to the physical movements and coordination of the speech organs (tongue, lips, teeth, etc.) to produce specific speech sounds. It involves the precise positioning and timing required for accurate sound production.
- Prosody: Prosody refers to the rhythm, stress, intonation, and melody of speech. It encompasses the variations in pitch, volume, tempo, and emphasis that convey additional meaning, such as emotional expression, emphasis, or linguistic distinctions.
- Fluency: Fluency relates to the smoothness and flow of speech. It involves the ability to produce speech effortlessly, without interruptions, hesitations, or disfluencies (e.g., stutters or repetitions).
Language and speech are closely intertwined, as speech serves as a means to express language. Language provides the underlying structure and rules, while speech allows individuals to articulate and produce language in a spoken form for communication. Both language and speech are essential for effective interpersonal communication and play significant roles in human interaction and socialization.
LANGUAGE AND ITS COMPONENTS
Language is a system of symbols shared by a group of people.
COMPONENTS OF LANGUAGE

Phonetics and Phonology
Phonetics is the study of the physical sounds produced in speech, while phonology focuses on the organization and patterns of those sounds within a language. It deals with phonemes (distinct units of sound) and their combinations.
Morphology
Morphology is the study of the structure of words and how they are formed. It examines morphemes, which are the smallest meaningful units of language. Morphology explores the ways in which morphemes can be combined to create words, such as prefixes, suffixes, and root words.
Syntax
Syntax refers to the rules and principles governing the arrangement of words to form meaningful phrases, clauses, and sentences. It involves the study of sentence structure, word order, and grammatical relationships between words.
Semantics
Semantics deals with the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences. It examines how words and expressions convey meaning and how meaning is interpreted in different contexts. Semantics also explores the relationships between words and their referents.
Lexicon
The lexicon comprises the vocabulary of a language. It includes all the words, their meanings, and the information associated with them, such as pronunciation, usage, and grammatical properties.
Pragmatics
Pragmatics focuses on the study of how language is used in context to achieve communicative goals. It explores the role of context, speaker intentions, and social factors in interpreting meaning and understanding implied messages.
Discourse
Discourse refers to the extended use of language beyond the level of individual sentences. It involves the study of how sentences and utterances are connected to form coherent and meaningful texts or conversations.
These components work together to create a complex and dynamic system that enables effective communication in English. Understanding these components can help in learning and mastering the language.
COMMUNICATION AND ITS COMPONENTS
Communication is the process of transmitting information, ideas, thoughts, and feelings from one individual or group to another. It plays a vital role in human interaction and is essential for social, professional, and personal relationships. Language, on the other hand, is a system of communication that utilizes symbols, such as words, sounds, or gestures, to convey meaning. Language is a crucial tool for communication, enabling individuals to express their thoughts, share information, and understand one another.
The relationship between communication and language is intertwined. Language is the medium through which communication occurs. It provides the structure and framework for expressing ideas and conveying messages. Communication, on the other hand, encompasses the broader process of exchanging information, which can occur through various means, including verbal and nonverbal communication.
Communication is typically a proactive and deliberate activity. As a result, people may switch roles. The speaker transmits information (a message) and the listener voluntarily accepts it. Additionally, it is possible to communicate without consciously trying. For instance, expressions of displeasure that we wish to conceal can be seen in the eyes, body language, tone, etc. Different forms of transmission are available for the message. Instead, we communicate using all available sensory modalities.
Examples of communication
Communication methods that involve hearing or speaking include speaking, telephone, siren, alarms, and so on.
Examples of seeing-based communication methods
Reading, writing, telegrams, gestures, facial expressions, and body positions. movies, dance, drama, and television Examples of ways to communicate through touch and smell Handshakes, kisses, hugs, punches, slaps,
MODES OF COMMUNICATION
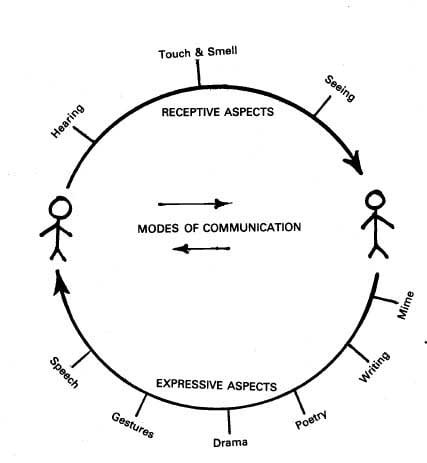
The modes of communication encompass different channels through which messages are transmitted. These modes can be broadly categorized into verbal, non-verbal, written, and visual communication.
Verbal Communication: The Power of Spoken Words
Verbal communication is the most common and direct form of communication. It involves the use of spoken words to convey messages. Whether through face-to-face conversations, phone calls, or public speaking, verbal communication enables real-time interaction. It allows individuals to express their thoughts, opinions, and emotions effectively.
Face-to-Face Communication: Building Meaningful Connections
Face-to-face communication is a powerful mode of interaction, enabling immediate feedback and non-verbal cues. It fosters personal connections, builds trust, and enhances understanding. Meeting someone in person allows for a deeper level of engagement, making it an invaluable mode of communication in both personal and professional settings.
Phone Calls: Bridging the Distance
In an increasingly globalized world, phone calls provide a convenient way to communicate across long distances. Hearing someone’s voice can convey nuances and emotions that might be missed in written communication. Phone calls are particularly useful when immediate responses are required, making them an essential mode of communication in various scenarios.
Non-Verbal Communication: Beyond Words
Non-verbal communication involves transmitting messages without the use of spoken language. It relies on gestures, facial expressions, body language, and tone of voice to convey meaning. Non-verbal cues can significantly impact the interpretation of messages, sometimes even overpowering verbal communication.
Body Language: Speaking without Words
Body language plays a crucial role in communication. It includes posture, gestures, eye contact, and facial expressions. Being aware of body language helps in understanding others’ feelings and intentions, ensuring effective communication. A simple nod or a warm smile can reinforce the spoken message and foster better connections.
Visual Communication: Conveying Messages through Images
Visual communication utilizes images, charts, graphs, and symbols to convey information. It is an effective mode of communication, especially when dealing with complex data or concepts. Visual aids enhance comprehension, making information more accessible and memorable.
Written Communication: The Power of the Written Word
Written communication involves expressing thoughts and ideas through written symbols. It is a structured and precise mode of communication, allowing for careful crafting of messages. From emails to letters, written communication provides a permanent record that can be referenced later.
Emails: Efficient and Instant Correspondence
In today’s digital age, emails have become a primary mode of professional communication. They offer a quick and efficient way to exchange information, documents, and ideas. Emails allow for formal and informal correspondence, fostering collaboration and productivity in various fields.
Letters: The Art of Thoughtful Communication
Traditionally, the written letter holds a timeless charm. It allows individuals to express themselves thoughtfully and in a more personal manner. Letters are particularly cherished for their sentimental value, making them a popular choice for special occasions and formal communication.
Visual Communication: Conveying Messages through Images
Visual communication utilizes images, charts, graphs, and symbols to convey information. It is an effective mode of communication, especially when dealing with complex data or concepts. Visual aids enhance comprehension, making information more accessible and memorable.
References:
- Manual on Developing Communication Skill in Mentally Retarded Persons T.A. Subba Rao [Book]
- Speech Science Primer (Sixth Edition) Lawrence J. Raphael, Gloria J. Borden, Katherine S. Harris [Book]
You are reading about:
Components of Speech Language and Communication






0 Comments