Phonetic Inventory Phonemic Inventory and Phonotactic Inventory: Phonetic Inventory refers to the complete set of distinct speech sounds utilized in a specific language. It encompasses both consonants and vowels, capturing the subtle variations in pronunciation that differentiate one word from another. Phonemic Inventory deals with the phonemes present in a language. Phonemes are the minimal units of sound that can alter the meaning of a word when substituted for one another. Phonotactic Inventory plays a crucial role in shaping the structure and patterns of language. It refers to the set of rules that govern the permissible arrangement of phonemes in a specific language.
| Table of Content |
|
Phonetic Inventory
The Phonetic Inventory refers to a comprehensive list of speech sounds that an individual produces, regardless of whether they are part of their native language or not. It includes all the distinct sounds the person can create, encompassing both consonants and vowels. Understanding an individual’s Phonetic Inventory helps identify the specific speech sounds they struggle with, leading to tailored therapeutic interventions.
In speech therapy, we thoroughly assess a person’s Phonetic Inventory through various activities and tests. By doing so, we gain insights into their speech patterns, which enables us to design targeted treatment plans to enhance their communication abilities effectively.
English Phonetic Inventory
For the English language, the Phonetic Inventory comprises a diverse set of sounds produced by native speakers and non-native speakers alike. English has a vast array of consonant and vowel sounds, each playing a unique role in forming words and conveying meaning.
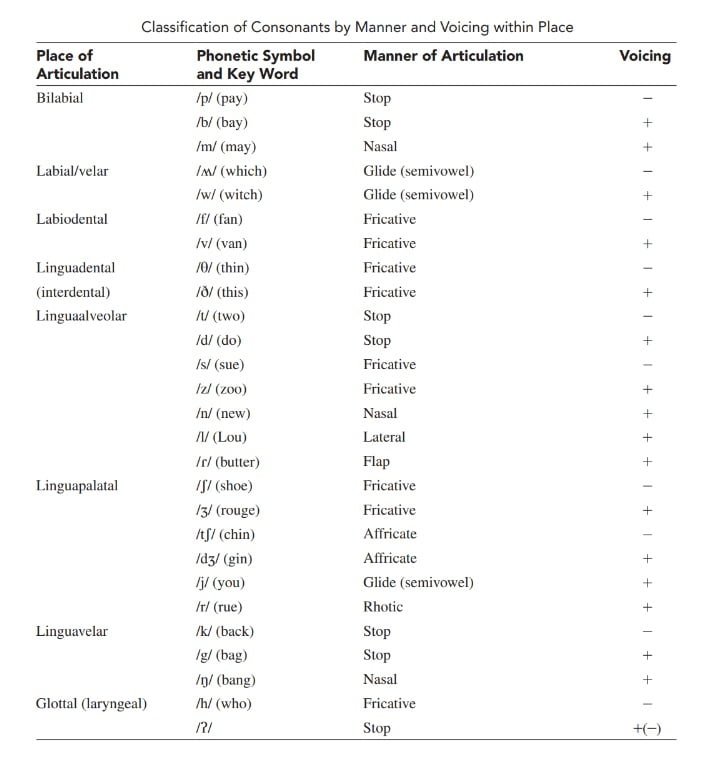
English Consonant Phonetic Inventory
Consonants in English may include familiar sounds like /p/, /b/, /t/, /d/, /k/, /g/, /m/, /n/, /s/, /z/, /f/, /v/, /h/, /r/, /l/, /w/, and /j/. However, there are also less common sounds like the voiceless dental fricative /θ/ as in “think” or the voiced postalveolar fricative /ʒ/ as in “measure.”
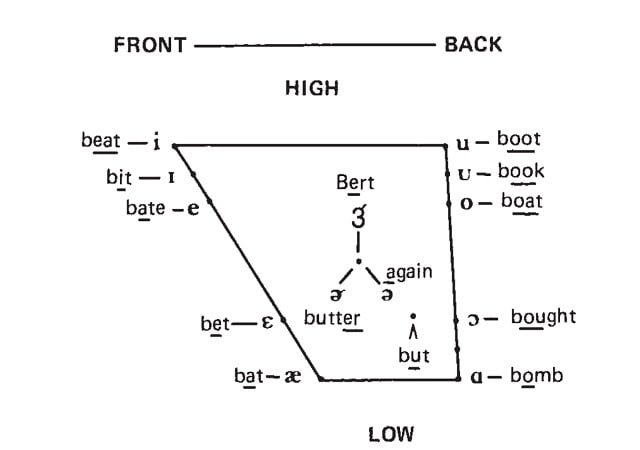
English Vowel Phonetic Inventory
The English vowel sounds are equally diverse and encompass /iː/, /ɪ/, /e/, /ɛ/, /æ/, /ɑː/, /ʌ/, /ɜː/, /ʊ/, /uː/, /ɔː/, and /oʊ/ among others. These vowels are essential in shaping the pronunciation and meaning of words, making them crucial elements of the Phonetic Inventory.
Phonemic Inventory
Phonemic Inventory, on the other hand, refers to a more abstract and linguistically significant collection of sounds in a language. It consists of the phonemes, which are the smallest units of sound that can distinguish meaning in a particular language. Unlike the Phonetic Inventory that lists all sounds produced, the Phonemic Inventory focuses on identifying the distinctive sound units that carry meaning and differentiate words from one another.
In English, the phonemes are responsible for creating minimal pairs, which are words that differ in meaning by only one sound. For example, the words “pat” and “bat” are minimal pairs because the initial sounds /p/ and /b/ change, altering the meaning of the word.
English Phonemic Inventory
The English language has a complex Phonemic Inventory, as it encompasses numerous phonemes that create the rich vocabulary and expression present in the language. For instance, the phonemes /p/, /b/, /t/, and /d/ are part of the English language’s consonant inventory, each having a specific role in constructing meaningful words.
When considering vowels, the English Phonemic Inventory includes phonemes such as /iː/, /eɪ/, /aɪ/, /aʊ/, /oʊ/, /ɔɪ/, /uː/, /ɜːr/, /ɑːr/, and /ər/, among others. These vowel phonemes contribute to the diversity of English words, enabling effective communication and expression.
Phonotactic Inventory
The Phonotactic Inventory encompasses the permissible combinations and arrangements of phonemes within a language. It defines the rules and restrictions governing how sounds can be arranged in syllables and words.
Understanding the Phonotactic Inventory is crucial in speech therapy as it aids in assessing speech disorders and identifying patterns of difficulty. By recognizing phonotactic patterns, speech therapists can formulate targeted interventions to improve an individual’s ability to produce and combine sounds accurately.
In English, the Phonotactic Inventory allows for various combinations of consonants and vowels, leading to a plethora of words and linguistic possibilities. These phonotactic patterns facilitate smooth speech production and aid in achieving linguistic fluency.
Phonetic Inventory vs. Phonemic Inventory: Unraveling the Distinctions
In the world of linguistics and speech therapy, the terms “Phonetic Inventory” and “Phonemic Inventory” hold crucial significance. Both concepts revolve around the study of speech sounds, but they differ in their scope and application. In this article, we will explore the distinctions between Phonetic Inventory and Phonemic Inventory, shedding light on how each plays a unique role in understanding language development and speech disorders.
Phonetic Inventory: An Exploration of Speech Sounds
The Phonetic Inventory refers to an exhaustive list of all the speech sounds produced by an individual, irrespective of their linguistic background. It encompasses both consonants and vowels, comprising the full range of sounds that a person can articulate. The Phonetic Inventory takes into account not only the sounds present in the individual’s native language but also those from other languages they might have encountered.
In speech therapy, the assessment of a person’s Phonetic Inventory is crucial. By analyzing the complete set of sounds they can produce, speech therapists gain valuable insights into their articulation abilities and identify any speech disorders or difficulties. This comprehensive analysis serves as the foundation for tailored intervention plans aimed at improving the individual’s speech and communication skills.
Phonemic Inventory: Decoding the Building Blocks of Language
On the other hand, the Phonemic Inventory focuses on a more abstract and linguistic aspect of speech sounds. It specifically deals with phonemes, which are the smallest units of sound that can differentiate meaning in a given language. Phonemes are essential because they allow us to distinguish one word from another, even if the sounds differ by just one element.
For example, in English, the words “pat” and “bat” are minimal pairs, where the only difference is the initial sound /p/ and /b/. The existence of such minimal pairs highlights the significance of phonemes in constructing meaningful words and conveying precise messages.
Comparing Phonetic Inventory and Phonemic Inventory
The primary difference between Phonetic Inventory and Phonemic Inventory lies in their scope and purpose:
Scope
- Phonetic Inventory covers all speech sounds a person can produce, including both native and non-native sounds.
- Phonemic Inventory, on the other hand, focuses solely on the distinctive sound units (phonemes) that carry meaning in a specific language.
Purpose
- Phonetic Inventory is useful in identifying an individual’s articulation abilities and speech patterns, making it valuable for speech therapy assessment and intervention.
- Phonemic Inventory is vital for understanding the linguistic structure of a language and its ability to convey meaning through different combinations of phonemes.
Implications for Speech Therapy and Language Development
The distinction between Phonetic Inventory and Phonemic Inventory has profound implications for speech therapy and language development:
Speech Therapy
- Phonetic Inventory assessment helps speech therapists pinpoint specific speech sounds that individuals struggle with, guiding the creation of personalized treatment plans.
- Phonemic Inventory analysis allows therapists to identify phonological difficulties, leading to targeted interventions to improve phonological awareness and speech clarity.
Language Development
- Understanding the Phonemic Inventory of a language aids in early language development in children. It helps them recognize and produce the distinct sounds that form the foundation of communication.
- Expanding one’s Phonetic Inventory by learning new speech sounds can enhance language learning and communication across different linguistic contexts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Phonetic Inventory and Phonemic Inventory are two essential concepts in the study of speech therapy and language development. While Phonetic Inventory encompasses all speech sounds produced by an individual, Phonemic Inventory focuses on the distinct phonemes that carry meaning in a language. Each serves a unique purpose in understanding and improving speech and communication abilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is a Phonetic Inventory?
- A Phonetic Inventory refers to a comprehensive list of speech sounds that an individual can produce, regardless of their native language. It includes both consonants and vowels.
2. What is the significance of understanding an individual’s Phonetic Inventory?
- Understanding an individual’s Phonetic Inventory helps identify specific speech sounds they may struggle with, leading to tailored therapeutic interventions, especially in speech therapy.
3. What does the English Phonetic Inventory encompass?
- The English Phonetic Inventory comprises a diverse set of consonant and vowel sounds, which are crucial in shaping the pronunciation and meaning of words.
4. What is a Phonemic Inventory?
- A Phonemic Inventory deals with the phonemes present in a language, which are the smallest units of sound that can alter the meaning of a word when substituted for one another.
5. How does the Phonemic Inventory differ from the Phonetic Inventory?
- The Phonemic Inventory focuses on identifying the distinctive sound units (phonemes) that carry meaning and differentiate words, whereas the Phonetic Inventory lists all sounds produced by an individual, including those from other languages.
6. What is an example of a minimal pair in English that demonstrates the significance of phonemes?
- An example of a minimal pair in English is “pat” and “bat,” where the only difference is the initial sound (/p/ and /b/), which changes the meaning of the word.
7. What does the Phonotactic Inventory refer to?
- The Phonotactic Inventory encompasses the permissible combinations and arrangements of phonemes within a language, defining the rules and restrictions governing how sounds can be arranged in syllables and words.
8. Why is understanding the Phonotactic Inventory important in speech therapy?
- Understanding the Phonotactic Inventory is crucial in speech therapy because it aids in assessing speech disorders and identifying patterns of difficulty, which helps formulate targeted interventions to improve speech accuracy.
9. How can the knowledge of Phonetic Inventory and Phonemic Inventory be applied in speech therapy?
- The knowledge of Phonetic Inventory helps speech therapists identify specific speech sounds individuals struggle with, leading to personalized treatment plans. Phonemic Inventory analysis helps identify phonological difficulties, leading to targeted interventions to improve phonological awareness and speech clarity.
10. How does understanding the distinctions between Phonetic Inventory and Phonemic Inventory benefit language development?
- Understanding the distinctions between these two concepts can aid in early language development by helping individuals recognize and produce the distinct sounds that form the foundation of communication. Additionally, expanding one’s Phonetic Inventory by learning new speech sounds can enhance language learning and communication across different linguistic contexts.
References:
- A Course in Phonetics Sixth Edition – PETER LADEFOGED [Book]
- An Introduction to English Phonetics – Richard Ogden [Book] [Book]
- Articulation and Phonological disorder Speech Sound Disorders in Children 8th Edition – John E Bernthal [Book]
- Assessment in Speech Language Pathology A Resource Manual 5th Edition, Kenneth G. Shipley, Julie G. McAfee [Book]
- Manual on Developing Communication Skill in Mentally Retarded Persons T.A. Subba Rao [Book]
You are reading about:
Phonetic Inventory Phonemic Inventory and Phonotactic Inventory


0 Comments