
Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment 2 (FDA 2): Scoring | Interpretation: The Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment (FDA) stands as a pivotal advancement in the clinical management of dysarthria, a prevalent acquired speech disorder resulting from neuromuscular disorders. Despite the increasing sophistication of technological methods for assessing neuromotor activity, the field has grappled with a lack of standardized clinical tools replicable in treatment settings. Crafted at Frenchay Hospital, the FDA emerges as a comprehensive and standardized test, enabling speech pathologists to definitively diagnose dysarthria. Having been administered to over 600 patients by a network of more than 200 speech therapists, the FDA addresses the need for a reliable, efficient, and user-friendly protocol in the assessment and management of dysarthria.
This article explores the intricacies of the Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment 2 (FDA 2), outlining its protocol, categories, scoring methods, and the essential equipment required for its administration. Understanding the FDA 2 is critical not only for speech pathologists but also for interdisciplinary clinical teams involved in the diagnosis and treatment of patients exhibiting dysarthric symptoms.
- Author: Pamela M Enderby
- Publication Date: 2008
- Age Range: 12 years to adult
- Administration Time: 20 to 40 Minutes
Table of Contents |
|
What is Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment (FDA)?
Dysarthria is a term employed to characterize speech irregularities stemming from neuromuscular disorders. Although dysarthria stands out as the most prevalent acquired speech disorder, there has been limited headway in its clinical management. Despite the availability of sophisticated technological methods for assessing neuromotor activity, there is a lack of a clinical tool replicable in treatment settings. The Dysarthria Assessment, crafted at Frenchay Hospital, emerges as a standardized test enabling speech pathologists to definitively diagnose dysarthria. This test has been administered to more than 600 patients by over 200 speech therapists.
Protocol for Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment 2 (FDA)
The protocol necessary for a dysarthria test should ensure that the obtained results are easily applicable to therapy. Dysarthria often presents speech that is perplexing for speech therapists, making it crucial to describe both the affected and unaffected areas of speech in relation to each other. This comprehensive understanding is essential for devising an appropriate treatment plan. The test results should also be sensitive to changes in speech patterns to assess the relevance and impact of treatment procedures on the disorder. While recorded samples are helpful, audio tapes have limitations in interpreting dysarthric speech.
Efficiency and user-friendliness are essential attributes of the test. The test format must be clear and practical to discourage therapists from modifying procedures to expedite the administration, and it should consider patients with poor stamina.
Standardization is key for a reliable test. A standardized administration ensures test-retest and intra/inter-judge reliabilities, facilitates the acquisition of normative data, and allows comparison with specific abnormal groups. Other dysarthria assessment methods may be available, but their lack of standardization renders them more like clinical checklists, limiting their value.
To achieve high reliability, minimal training should be required. Special attention to the test procedure and scoring system is crucial to minimize training for speech pathologists. Lengthy or expensive training may indicate a design flaw in the test, undermining the reliability of administration and scoring.
Communication of test results should be straightforward and inclusive of other professions, especially if the speech pathologist is part of a clinical team. Additionally, patients exhibiting dysarthric symptomatology can play a role in identifying or confirming a medical diagnosis.
Equipments for Administer FDA-2
1. Test manual
2. Scoring graph
3. Tongue depressor
4. Stopwatch
5. Tape recorder
6. Glass of water
7. Word cards
Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment 2 (FDA 2) Subtests
The examination is segmented into 8 primary subtests:
- Reflex
- Respiration
- Lips
- Jaw
- Palate
- Laryngeal
- Tongue
- Intelligibility
Influencing factors of learning
- Sight
- Teeth
- Language
- Mood
- Posture
- Rate and Sensation
Each major category consists of subtests. While it is recommended to follow the sequence on the chart for testing each section, it is not obligatory. Assess each subtest within the section as per the specified order. Adhere to the procedure and determine which grade best characterizes the patient’s behavior. Conducting the assessment in a relaxed interview style becomes feasible with familiarity with the test.
Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment 2 (FDA 2) Scoring
Certain grades encompass various behaviors within their definitions. The patient doesn’t need to display all behaviors to attain a specific grade. For instance, a patient expressing concern about taking longer to eat due to fear of coughing, even without coughing, falls under a certain grade. Similarly, a patient who occasionally chokes but remains unaware or indifferent is scored within that grade.
In cases where the patient’s behavior does not precisely align with a specific grade, the assessor can assign a score on the “in-between” lines, indicating the degree of difficulty. For instance, if the patient’s performance on an item is slightly worse than one grade but slightly better than the grade below, mark the line between these two grades.
The test necessitates the therapist to analyze each component’s behavior in isolation to assess relative abilities and disabilities. While speech is a unified system, impairment in one aspect often influences another’s behavior. Despite this challenge, the assessor must focus on each area separately, avoiding confusion caused by abnormalities in other areas. Adhering to the test procedure will enhance concentration.
It is essential to note that the tester should assign a score based on the behavior demonstrated during the second attempt of the specified tasks. The first attempt is primarily for practice purposes, and if the patient attempts the task a third time, it should not influence the scoring. Once the score is determined, use a ballpoint pen to draw a bold line on top of the printed one in that position on the graph. Matching on the graph need not be completed until the assessment is finished.
Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment 2 (FDA 2) Interpretation
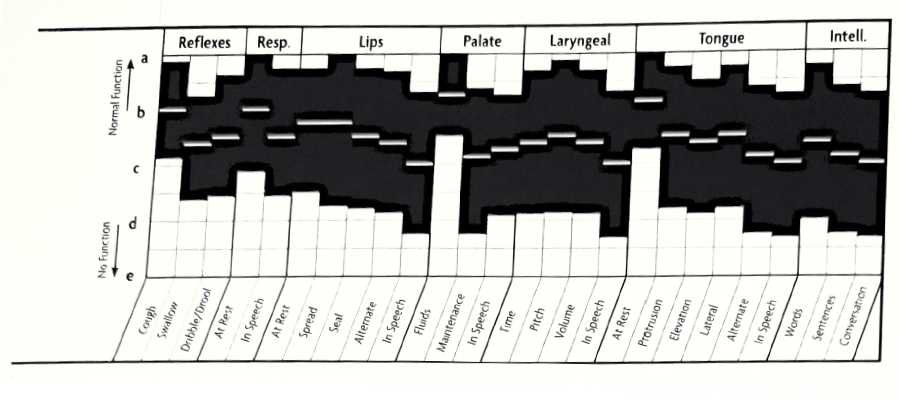
Upper Motor Neuron Lesions FDA Graph
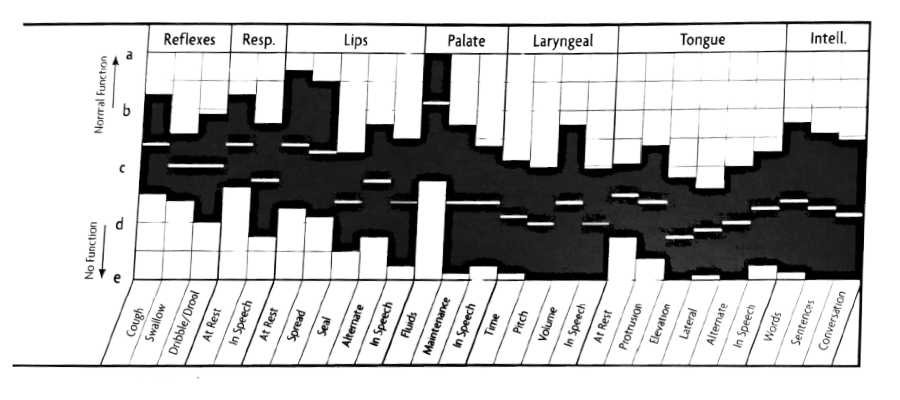
Mixed Upper and Lower Motor Neuron Lesions FDA Graph
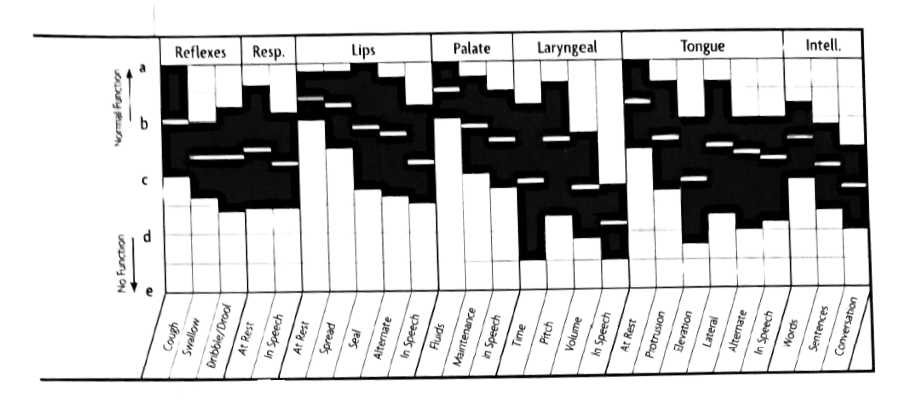

Extrapyramidal Lesions FDA Graph
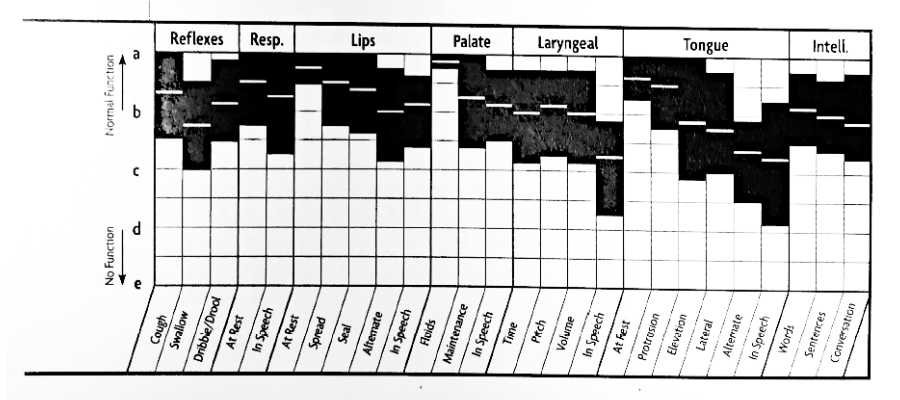
Cerebellar Lesions FDA Graph
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment (FDA) and its updated version, the Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment 2 (FDA 2), stand out as crucial tools in the diagnosis and management of dysarthria resulting from neuromuscular disorders. These standardized tests, developed at Frenchay Hospital, have proven their effectiveness through extensive administration to over 600 patients by a large number of speech therapists. The protocol for FDA 2 ensures the reliability of test results by emphasizing efficiency, user-friendliness, and standardization. The inclusion of specific categories and influencing factors provides a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s speech patterns, aiding in the formulation of targeted treatment plans. The simplicity and clarity of the scoring system, along with the recommended equipment, contribute to the ease of administration and interpretation. Overall, the FDA 2 emerges as a valuable resource that not only assists speech pathologists but also promotes interdisciplinary collaboration within clinical teams for improved patient care.
FAQs about Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment 2 (FDA 2): Scoring | Interpretation
1. What is the Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment?
The Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment (FDA) is a standardized test designed to diagnose dysarthria, a speech disorder resulting from neuromuscular disorders. Developed at Frenchay Hospital, this clinical tool is widely used by speech pathologists to comprehensively evaluate and diagnose dysarthria in patients, offering a structured approach for treatment planning.
2. How to score Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment?
Scoring the Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment involves assessing the patient’s performance across eight primary categories, including reflex, respiration, lips, jaw, palate, laryngeal, tongue, and intelligibility. The assessment utilizes a scoring graph, with grades and behavioral descriptions for each category. Assessors should focus on the patient’s behavior during the second attempt of specified tasks, avoiding influence from the first or subsequent attempts. In cases where behavior doesn’t align precisely with a grade, assessors can use “in-between” lines to indicate the degree of difficulty.
3. Is the Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment standardized?
Yes, the Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment is standardized. Standardization is a crucial aspect of the test, ensuring reliability through test-retest and intra/inter-judge reliabilities. It facilitates the acquisition of normative data and allows for meaningful comparison with specific abnormal groups. The standardized administration ensures consistency in results, making it a reliable tool for diagnosing dysarthria. Other assessment methods lacking standardization may function more like clinical checklists, limiting their value in clinical settings.
4. What equipments are needed to administer FDA-2?
To administer the Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment 2 (FDA 2), the following equipment is needed: a test manual, scoring graph, tongue depressor, stopwatch, tape recorder, glass of water, and word cards. These tools are essential for conducting a comprehensive assessment of the patient’s reflex, respiration, lips, jaw, palate, laryngeal, tongue, and intelligibility.
5. What are the influencing factors of learning in the FDA 2 assessment?
Various factors can influence the patient’s performance in the Frenchay Dysarthria Assessment 2, including sight, teeth, language, mood, posture, rate, and sensation. These factors are taken into account during the assessment to provide a holistic understanding of the patient’s speech capabilities and to tailor an appropriate treatment plan. Speech pathologists conducting the assessment should be aware of these influencing factors to ensure accurate and reliable results.


Thank u for what all u have sent till now .