Speech Reception Thresholds – Procedure and Application: The speech reception threshold is the minimum hearing level for speech (ANSI, 2010) at which an individual can recognize 50% of the speech material. Speech reception thresholds are achieved in each ear. The term speech reception threshold is synonymous with speech recognition threshold.
Purpose of Speech Reception Thresholds:
- To validate the thresholds obtained through PTA
- To serve as a reference point for supra-threshold tests
- To ascertain the need for aural (re)-habilitation and monitor its progress
- To determine hearing sensitivity in difficult to test population
Materials for Speech Reception Thresholds:
- Spondaic words are the usual and recommended test material for the SRT test. They are 2-syllable words that have equal stress on both syllables.
- Word familiarization can be done prior to the start of the test. This ensures that the client is familiar with the test vocabulary, and the client’s responses can be accurately interpreted by the clinician. Care to be taken to eliminate the visual cues during familiarization.
- Based on the circumstances or individuals (age, language facility, physical condition), the standard word list can be modified; however, the use of speech stimuli with less homogeneity than spondaic words may compromise the reliability of this measure.
- The test material used should be noted in the reporting of the results.
Response Format / Mode of Speech Reception Thresholds:
- The usual response mode for obtaining the SRT is the repetition of the stimulus item.
- For many patients it is not possible to obtain verbal responses, necessitating the use of alternative response modes such as writing down the responses or a closed set of choices such as picture pointing, signing, or visual scanning, etc.
- If picture pointing mode is to be used, then the clinician should be cautious in choosing the number of response items (e.g., between 6 and 12 words usually is appropriate).
Procedure of Speech Reception Thresholds:
There are different methods to obtain SRT, such as the ascending or descending method.
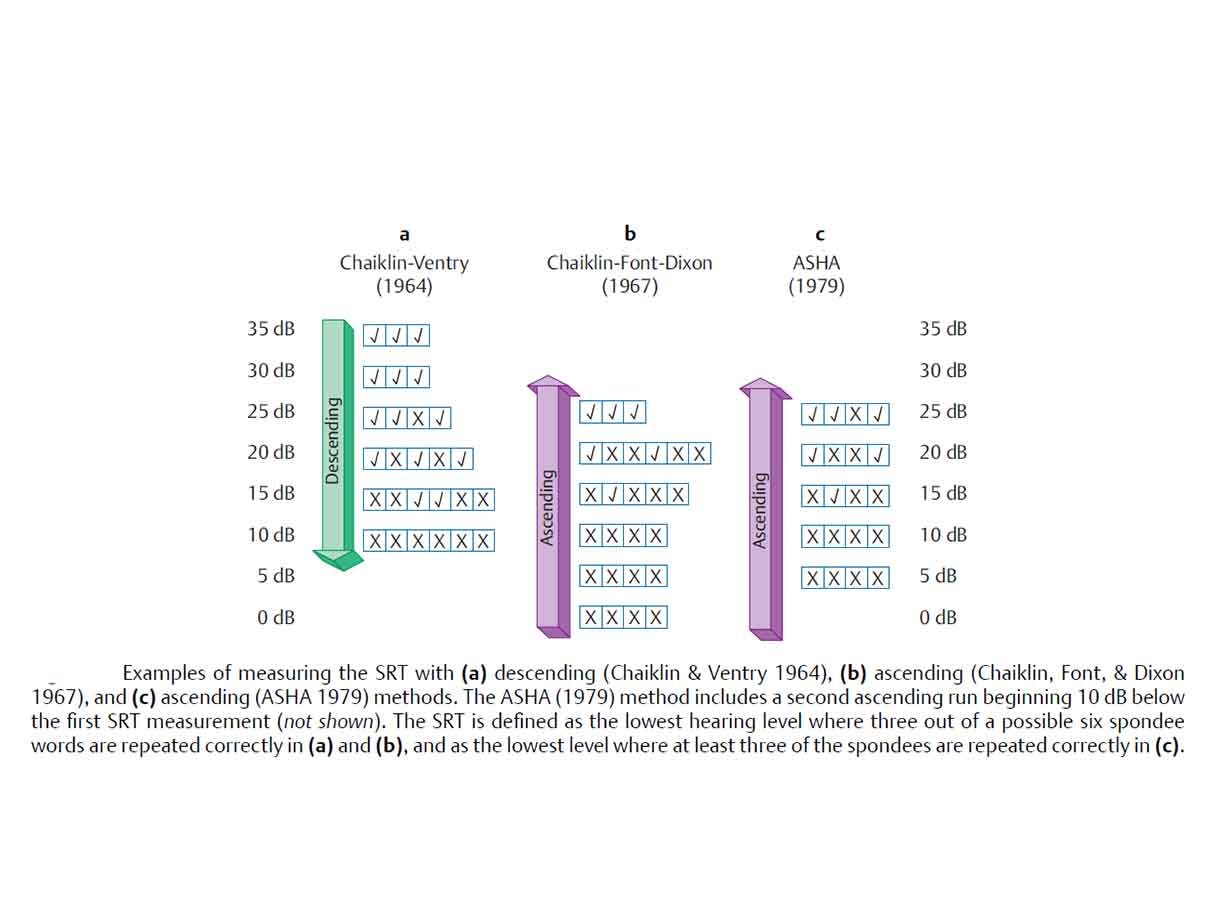
Generally, the descending method (ASHA, 1988) is preferred and is described below.
- Obtain pure tone average (PTA).
- Starting level for SRT: 30-40dB above anticipated SRT or 20 dBSL (with reference to PTA).
- Present one spondee at a time at this level. Decrease in 10 dB decrements, whenever the client response is correct. The 10 dB decrement continues until one word is missed/ until the client responds incorrectly.
- Now present a second spondaic word at the same level that the client responded incorrectly.
- If the second word is correctly identified by the client, the level is attenuated by 10 dB, and two spondees are presented. This process is continued until two spondees are incorrectly identified at one level. This is the preliminary phase and the actual test phase begins, which can be performed in a 5 dB step (Martin & Sides, 1985).
- If you get a response for at least one spondee, reduce the intensity by 5 dB and present 03 spondees at that level.
- Continue the same procedure, until “no response” for all the 03 spondees obtained. Increase by 5 dB and continue it by presenting 03 spondees at each level till you get 2/3 spondees (>50%). That level can be considered as SRT.
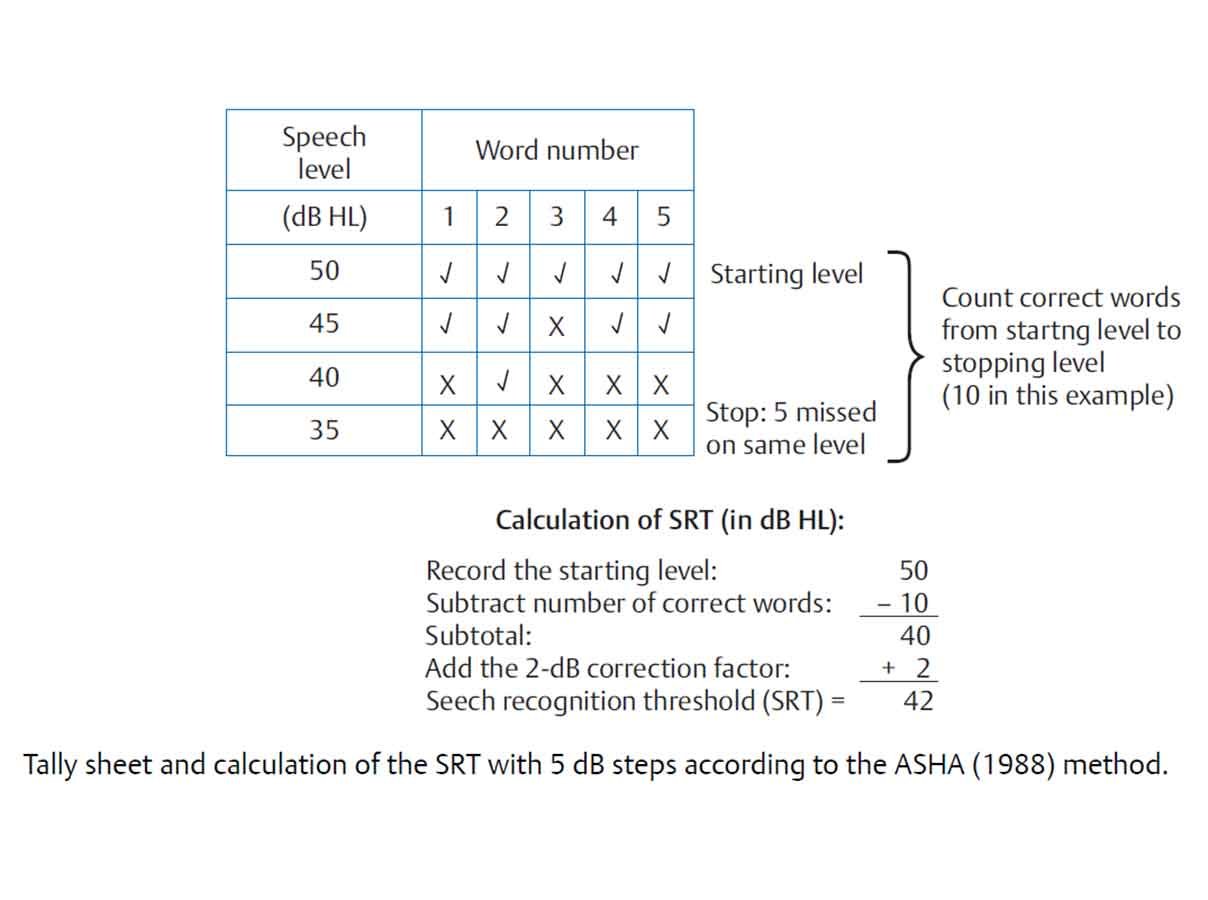
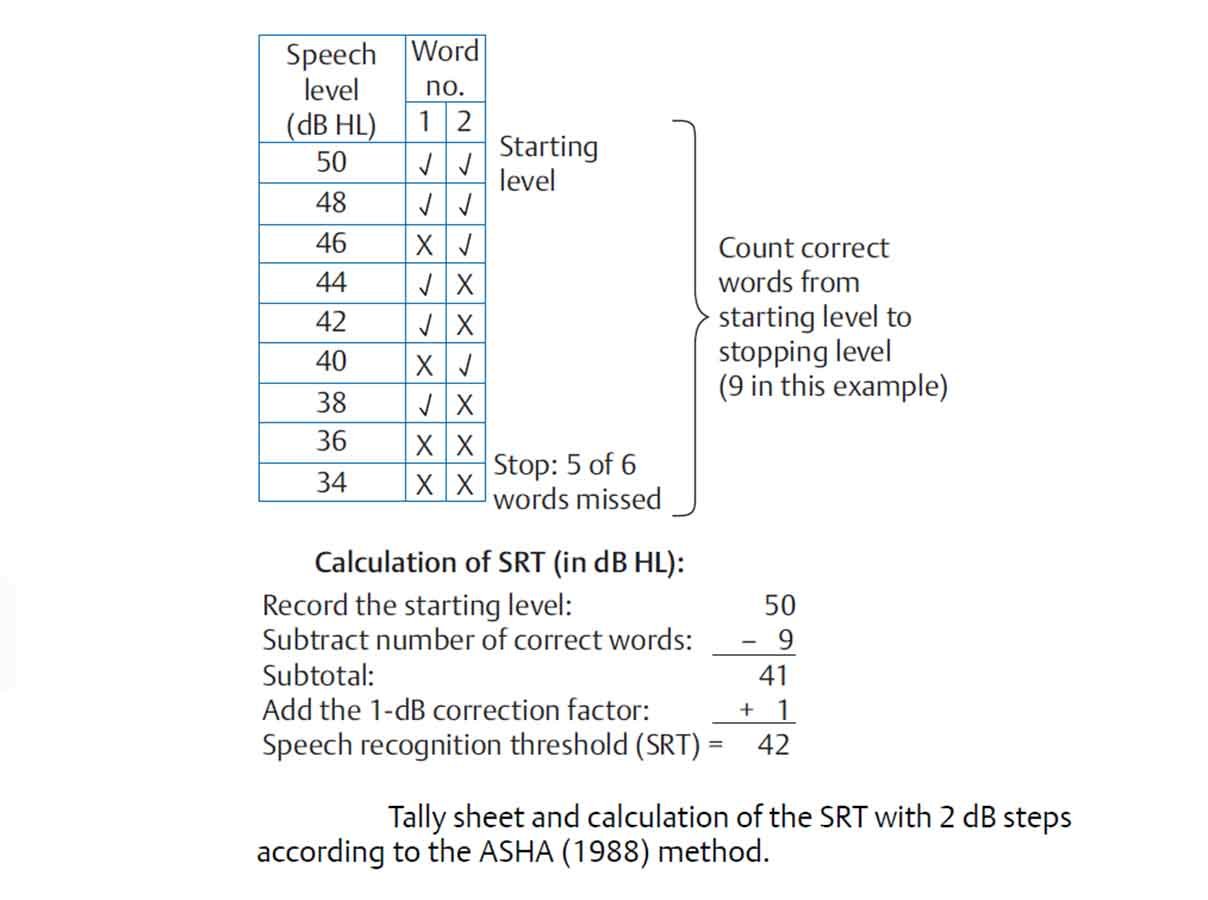
Interpretation of Speech Reception Thresholds:
- The SRT must be documented in dB HL. The results should be documented for each ear on the same form as the client’s results for pure tone audiometry. There should be enough space to document additional relevant information that describes the test environment, such as alternate materials or response formats.
- The SRT & PTA correlation are usually within 6 – 12dB.
- If there is disagreement, it could indicate one of the possibilities: misunderstanding of the instructions, functional hearing loss (non-organic), instrumentation malfunction, pathology along CANS including VIII nerve, cognitive and language difficulties, etc. For e.g. the SRT can be poorer than PTA in elderly and auditory processing disorders; whereas the SRT can be better than PTA in cases of malingerers/functional hearing loss.
Masking of Speech Reception Thresholds:
- Masking should be applied to the non-test ear, when the obtained SRT in one ear exceeds the apparent SRT or a pure tone BC threshold at 500, 1000, 2000 or 4000 Hz in the contralateral ear by 40 dB or more.
- The masker used should have a wide band spectrum (white, pink or speech noise) to effectively mask the speech stimuli.
- The level of effective masking used should be sufficient to eliminate reception by the non-test ear without causing over masking and should be recorded on the same form as that used to record audiometric results.
Application of Speech Reception Thresholds:
Speech recognition measures have been used in every phase of audiology, such as
- To describe the extent of hearing impairment in terms of how it affects speech understanding,
- In the differential diagnosis of auditory disorders,
- For determining the needs for amplification and other forms of audiologic rehabilitation,
- For making comparisons between various hearing aids and amplification approaches,
- For verifying the benefits of hearing aid use and other forms of audiologic rehabilitation, and
- For monitoring patient performance over time for either diagnostic or rehabilitative purposes.
References:
- https://www.ishaindia.org.in/pdf/Guidelines-Standard-Audiometric-Screening-Procedures.PDF
- https://www.asha.org/PRPSpecificTopic.aspx?folderid=8589935335§ion=Assessment#Speech_Audiometry
- Essentials of Audiology – Stanley A. Gelfand, PhD (Book)
You are reading about:
Speech Reception Thresholds – Procedure and Application







0 Comments