What is Speech Audiometry Test: Speech Audiometry includes Speech Awareness/Detection Thresholds (SDT/SAT), Speech Reception/Recognition Thresholds (SRT), Word Recognition Testing/Score (WRS), and sensitized speech testing (filtered, compressed, speech in noise, etc.) and is used to evaluate hearing sensitivity and speech perception ability and for site-of-lesion testing.
Speech audiometry is the method used to evaluate a person’s hearing threshold for speech sounds.
Since speech is the primary modality of human communication and the primary mode by which we interact with each other, it should not be surprising that speech is our most salient signal. Hence, the Pure Tone Audiogram presents only part of the patient’s auditory situation since it does provide any direct indication about his ability to hear and to understand speech. The researched method to know how a patient hears speech is called Speech Audiometry, which includes testing of patient with speech stimuli.
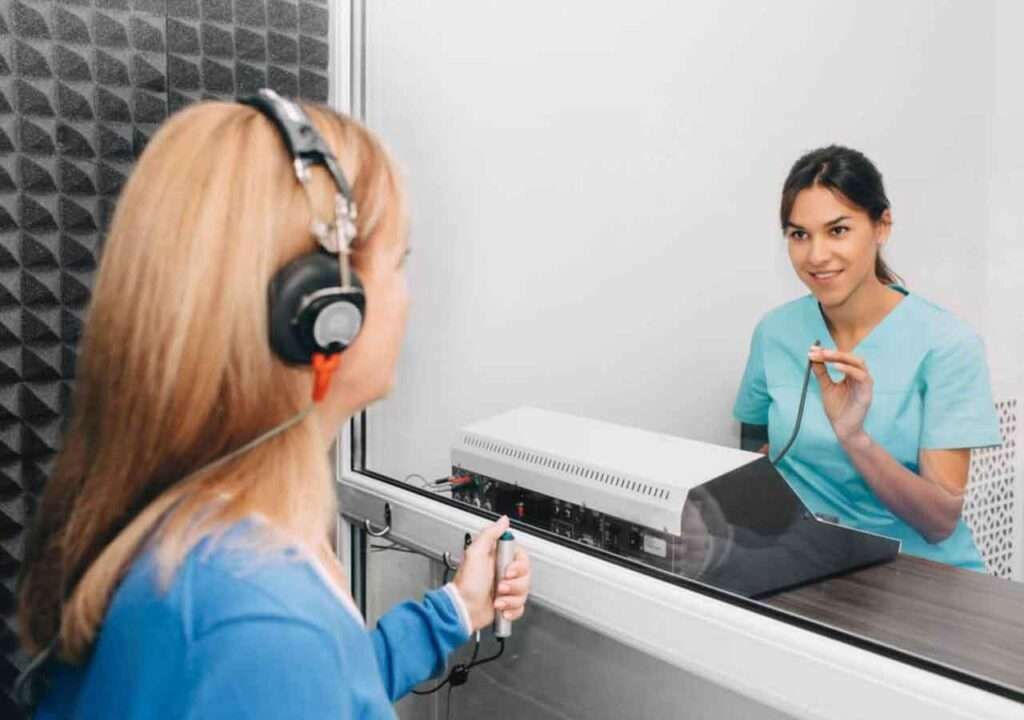

Instrument used for Speech Audiometry Test:
Speech Audiometry Test In the speech audiometry test, the instrument used is the speech audiometer. While dedicated devices for Speech Audiometry (Speech Mode/Channel of a clinical Audiometer) were previously employed, it is integrated into general-purpose clinical audiometers today.
Historical perspective of Speech Audiometry Test:
Speech audiometry is used to describe procedures which employ speech stimuli to measure auditory function (Konkle and Rintelmann, 1983). Such issues were experimentally addressed by Carhart (1951) whose work on speech audiometry established the common practice of assessing sensitivity for speech but also assessment of clarity when speech is heard. These ideas were outlined by Plomp (1978), in his model of hearing loss, as an audibility component (i.e., loss of sensitivity) and a distortion component (i.e., loss of clarity). The audibility part is measured via speech perception in quiet. The distortion component corresponds to a decreased ability to comprehend speech, particularly in background noise, irrespective of the presentation level. The distortion component is usually quantified by the Speech Recognition Score (SRS), which basically uses the percent correct recognition at Suprathreshold Levels. Recently (Killion et al., 2004; Wilson, 2003), the signal-to-noise ratio (S/N = [correct] /[noise]) at which 50% correct recognition is obtained has been suggested as a better objective than SRS.
References:
- https://www.asha.org/PRPSpecificTopic.aspx?folderid=8589935335§ion=Assessment#Speech_Audiometry
- https://www.ishaindia.org.in/pdf/Guidelines-Standard-Audiometric-Screening-Procedures.PDF
- Essentials of Audiology – Stanley A. Gelfand, PhD (Book)
- Handbook of Clinical Audiology – JACK KATZ, Ph.D. (Book)
You are reading about:
What is Speech Audiometry Test







Very helpful article for audiology student
Thank you!