Word Recognition Scores – Procedure and Application: The word recognition score is the percentage of words correctly identified at a constant suprathreshold level of presentation. Word Recognition Scores also known as Supra-Threshold Recognition Tests (Speech Discrimination Test SDT) or Sentence Recognition Score. The word recognition scores are obtained for each ear using phonetically balanced (PB) monosyllabic words and are reported as a percent correct. Various word lists can be found. If you make no mistakes, then testing can end after 10 words, and if you make no more than four mistakes, after 25. In all other cases the whole 50-item list is administered (Runge & Hosford-Dunn, 1985).
Purpose of Word Recognition Scores:
- To assess the individual’s auditory system’s capability to identify the speech stimuli.
Materials for Word Recognition Scores:
- Monosyllabic words that are presented in an open set format. These monosyllabic should be Phonetically balance PB words (sets of words that contain speech sounds with the same frequency of occurrence as in everyday conversation).
Examples:-
1- Picture Identification Task (PIT)
2- Central Institute of the Deaf (CID) W-22 word list
3- Word Intelligibility by Picture Identification (WIPI) Test
4- Northwestern University NU-Auditory Test # 6
5- Northwestern University Children’s Perception of Speech (NU-CHIPS)
Procedure of Word Recognition Scores:
- Instruct the pt. to repeat each test word.
- Adjust the attenuator to the desired presentation level (there are different ways);
30 or 35 +SRT …… (30dB if the audiogram is flat or 35 if it is slopping)
35 or 40 +SRT …….(35dB if the audiogram is flat or 40 if it is slopping) Or
MCL+ 5-10 dB…… (This is more accurate) - Use CARRIER PHRASE (say the word …) when you preset each word … WHY????>>>> To monitor stress and alert the patient that the test word was to follow.
- Remember to control the VU meter and avoid LIP READING.
- Then present the list of 50 monosyllabic words list or 25-word lists to avoid time-consuming
- Then press the correct or incorrect buttons in the audiometer for each response or calculate manually:
If you use 50 words list >>> give 2% for each correct response
If you use 25 words list >>> give 4% for each correct response
If you use 20 words list >>> give 5% for each correct response - Then record the percent correct score at the presentation level.
- Repeat the procedure for the other ear.
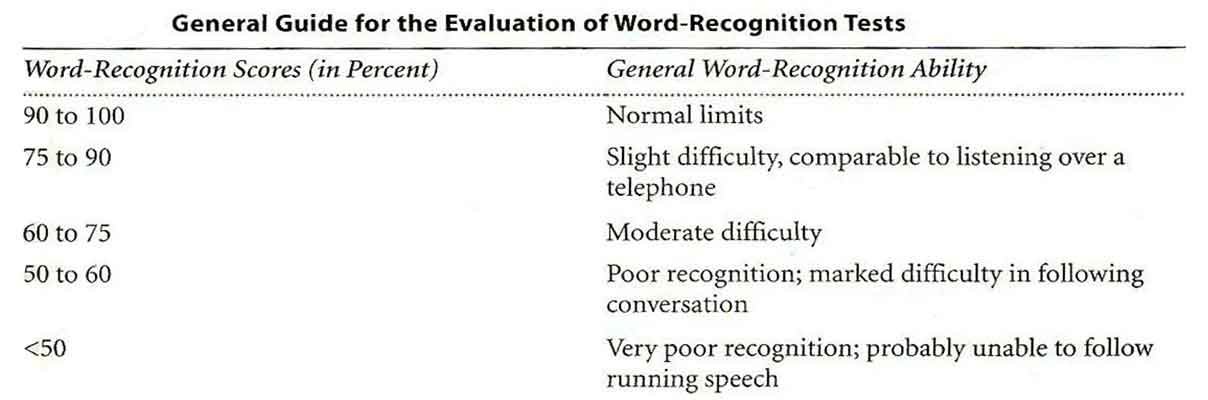
Interpretation of Word Recognition Scores:
- Record the percent correct score at the presentation level. As stated, when a 20 words list is used, 5% for each correct response is given.
- Normal: 90 to 100%; Conductive hearing loss: 80 or 60 to 100%; Cochlear pathology: >60%; Retro-cochlear pathology: < 70% (however, the scores vary depending on the etiology and degree of loss.

Masking of Word Recognition Scores:
Masking is used for word recognition testing when the presentation level in the test ear exceeds the best bone conduction threshold in any of the speech frequencies for the non-test ear (500, 1000, and 2000 Hz) by 35 dB or more (Roeser et al., 2007).
Children’s Word Recognition Scores:
Various monosyllabic word lists are available for determining the word recognition score for young children. The words from these lists are usually presented by MLV because of the flexibility needed when testing young children.
- PBK Test: The Phonetically Balanced Test of Speech Discrimination for Children (PBK-50)>>>uses an open response type task.
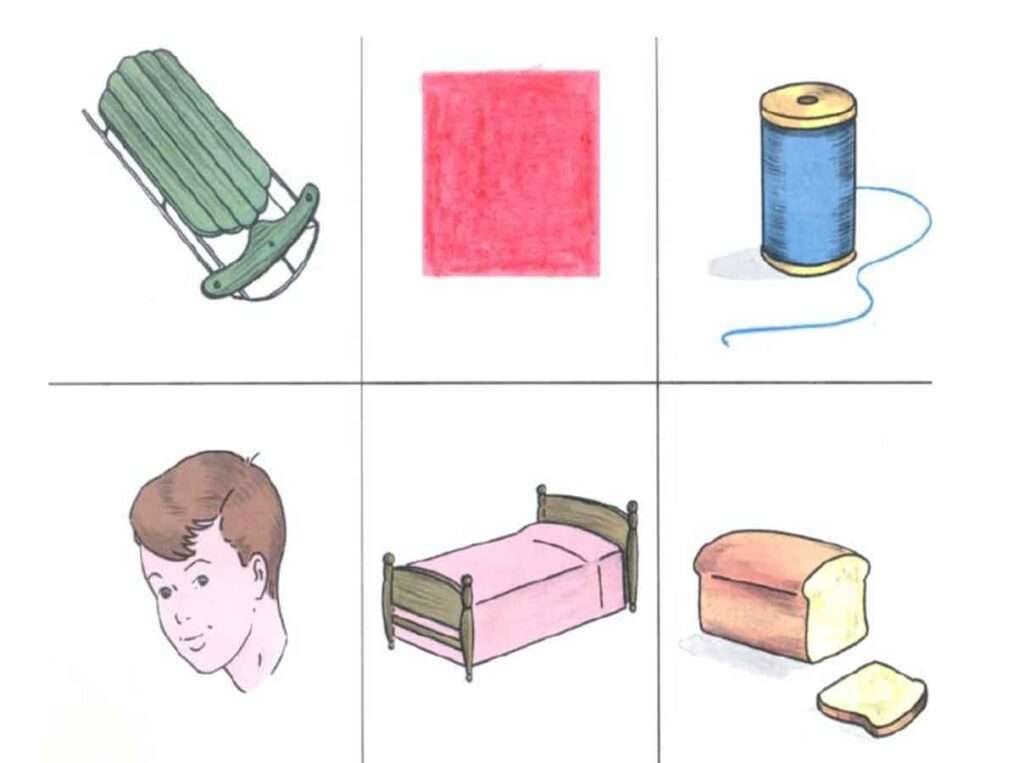
- WIPI Test (Word Intelligibility by Picture Identification)>>> uses a closed-response task(six pictures to chose from )
WIPI Sample Item:
- Northwestern University Children’s Perception of Speech (NUCHIPS) test – four pictures to choose
References:
- https://www.ishaindia.org.in/pdf/Guidelines-Standard-Audiometric-Screening-Procedures.PDF
- https://www.asha.org/PRPSpecificTopic.aspx?folderid=8589935335§ion=Assessment#Speech_Audiometry
- Essentials of Audiology – Stanley A. Gelfand, PhD (Book)
You are reading about:
Word Recognition Scores – Procedure and Application







Notes for neurology, audiology and speech