Types of Speech Therapy – Individual and Group Therapy: Speech therapy types can be valuable depending on the individual’s needs, and speech therapists may use a combination of approaches to create a comprehensive and personalized treatment plan.
Individual and Group Therapy: Individual speech therapy involves one-on-one sessions between the speech therapist and the client, tailored to their specific needs. Group speech therapy involves multiple clients working together in a small group setting, allowing them to practice communication skills and learn from each other.
Speech therapy plays a crucial role in helping individuals of all ages improve their communication abilities, overcome speech impediments, and enhance their quality of life.
Types of Speech Therapy
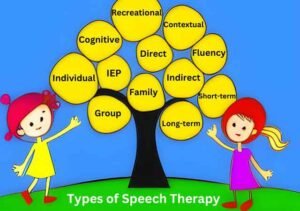
Types of Speech Therapy
- Individual and Group Speech Therapy
- Direct and Indirect Speech Therapy
- Individualized Education Plan (IEP)
- Fluency shaping therapy
- Short-term Speech therapy
- Long-term Speech therapy
- Cognitive therapy
- Contextual Therapy
- Family Therapy
- Recreational Therapy
1. Individual and Group Therapy
Speech therapy can be broadly categorized into two main types – individual therapy and group therapy. Both approaches have their unique advantages and are tailored to address various communication challenges.
Individual Speech Therapy
Individual therapy, as the name suggests, involves one-on-one sessions between the speech therapist and the client. This personalized approach allows the therapist to focus entirely on the individual’s specific speech needs, tailoring the therapy to suit their requirements. The sessions are designed to be intensive and goal-oriented, offering dedicated attention to the client’s speech development.
In individual therapy, the speech therapist conducts a thorough assessment of the client’s speech and language abilities. Based on the evaluation, a customized treatment plan is created, targeting areas that need improvement. The therapy may involve various techniques, such as articulation exercises, language drills, and assistive technology integration, to enhance the client’s communication skills.
Main Highlights of Individual Speech Therapy
- Personalized speech therapy
- Intensive sessions
- Customized treatment
- Articulation exercises
- Language drills
- Assistive technology.
Group Speech Therapy
Group therapy, on the other hand, involves small groups of individuals with similar speech challenges participating in therapy together. This collaborative approach fosters peer interaction and provides a supportive environment for individuals to practice their communication skills in real-life scenarios.
Group therapy sessions are beneficial for improving social communication and pragmatic language skills. Participants can engage in conversations, role-playing exercises, and group activities that simulate everyday communication situations. Working in a group setting can boost confidence, encourage empathy, and create a sense of camaraderie among the participants.
Main Highlights of Group Speech Therapy
- Collaborative therapy
- Peer interaction
- Social communication
- Pragmatic language skills
- Role-playing exercises
- Group activities.
Key Differences Between Individual and Group Therapy
Now that we have explored the basic concepts of individual and group therapy, let’s compare their differences to better understand which approach might be more suitable for specific individuals.
| Aspect | Individual Therapy | Group Therapy |
| Personalization | Tailored to individual needs and goals. | Addresses shared challenges in a group setting. |
| Attention | One-on-one focused attention from the therapist. | Shared attention among group members. |
| Social Interaction | Limited social interaction during sessions. | Enhanced social interaction and communication practice. |
| Motivation | Personalized goals can boost motivation. | Group dynamics can motivate participants. |
| Communication Practice | Targeted practice of individual speech skills. | Real-life communication practice with peers. |
Advantages of Individual Speech Therapy
Individual therapy offers several unique benefits that cater to specific speech-related challenges and individualized needs. Let’s explore some of these advantages:
- Tailored Treatment Plans: In individual therapy, treatment plans are customized to address the client’s specific speech and language difficulties. This personalized approach ensures that each session focuses on the areas that require improvement, maximizing the effectiveness of the therapy.
- Intensive Attention: Clients receive undivided attention from the speech therapist during individual sessions. This focused attention allows the therapist to closely monitor progress and make real-time adjustments to the therapy as needed.
- Flexibility: Individual therapy can be adapted and modified based on the client’s progress and changing needs. Therapists can employ different techniques and approaches to suit the client’s learning style and preferences.
- Privacy and Comfort: Some individuals may feel more comfortable expressing themselves in a private setting. Individual therapy provides a safe and confidential environment for clients to work on their speech challenges without feeling self-conscious.
- Accelerated Progress: Due to the focused and intensive nature of individual therapy, progress is often accelerated, leading to quicker improvements in speech and communication skills.
Disadvantages of Individual Speech Therapy
- It creates an artificial environment
- Parents have less social interaction with other parents of children with communication needs
- Generalization beyond the one-to-one Tx situation may not always occur
- The process takes more time for the therapist.
Advantages of Group Speech Therapy
Group therapy also offers a range of advantages that cater to different speech-related needs and social communication development. Let’s explore the benefits of group therapy:
- Social Interaction Skills: Group therapy allows participants to interact and communicate with peers facing similar challenges. This fosters the development of social interaction skills, such as turn-taking, active listening, and empathy.
- Real-Life Practice: Participants engage in real-life communication scenarios, which are often challenging to replicate in one-on-one settings. Group therapy provides a supportive space to practice these skills with immediate feedback from peers and the therapist.
- Peer Support: The camaraderie and support among group members can be highly motivating. Participants can learn from each other’s experiences, share coping strategies, and celebrate each other’s progress.
- Generalization of Skills: Skills learned in group therapy can be applied to various real-life situations, making it easier for individuals to generalize their improved communication abilities beyond the therapy setting.
- Building Confidence: Working and communicating in a group setting can boost self-confidence and self-esteem, encouraging individuals to take more initiative in social interactions.
Disadvantages of Group Speech Therapy
- Not all clients benefit from group therapy
- Some may be too shy or preoccupied.
- A shorter period spent on the person than with individual Tx
- Conflicts between individuals in the group may prevent the GP from reaching its goals.
- Clients may pick up undesirable behaviors from one another.
- The absence of some individuals could negatively impact the dynamics of the group.
- Confidentiality may be more challenging to maintain. Setting up a groups involves more organization and planning, as well as additional resources.
Which Approach is Right for You?
The choice between individual and group therapy depends on various factors, including the individual’s specific needs, communication goals, and comfort level in social settings. Here are some considerations to help you decide:
Individual Therapy is Ideal If:
- You have specific speech and language goals that require a personalized approach.
- You prefer one-on-one attention from the therapist.
- You have complex speech challenges that may need intensive focus.
Group Therapy is Ideal If:
- You want to improve social communication and pragmatic language skills.
- You feel motivated by working with peers facing similar challenges.
- You seek a supportive environment to practice communication skills.
It’s essential to discuss your preferences and objectives with a qualified speech therapist who can guide you towards the most suitable therapy approach for your needs.
In a nutshell, Speech therapy, encompassing individual and group therapy approaches, plays a vital role in helping individuals overcome speech and language challenges, enhance communication skills, and boost self-confidence. Each therapy type has its unique benefits, and the choice between them depends on the individual’s specific needs and objectives. Whether you opt for personalized attention in individual therapy or the support and camaraderie of group therapy, speech therapists are dedicated to helping you achieve your communication goals. Remember to seek professional guidance and choose the therapy approach that best aligns with your aspirations.
2. Direct and Indirect Speech Therapy
In direct speech therapy, the therapist works directly on specific speech or language goals with the client. Indirect speech therapy, on the other hand, involves addressing communication difficulties indirectly, such as by providing support and strategies to the client’s family or teachers.
Below is a table outlining some of the key techniques used in Direct and Indirect Speech Therapy along with their differences :
Technique | Direct Speech Therapy | Indirect Speech Therapy |
Description | Involves face-to-face interactions with the speech therapist. | Conducted remotely or virtually, often through video conferencing or speech therapy apps. |
Benefits | Allows for immediate feedback and personalized guidance. | Provides flexibility and accessibility for individuals who cannot attend in-person sessions. |
Articulation Exercises | Focuses on specific speech sounds and helps improve pronunciation. | Utilizes various exercises to target specific speech difficulties and enhance articulation. |
Voice Therapy | Concentrates on vocal quality, pitch, and volume control. | Aims to improve voice tone, resonance, and vocal projection. |
Language Training | Enhances language comprehension, vocabulary, and grammar. | Addresses language processing issues and supports language development. |
Fluency Improvement | Targets fluency disorders like stuttering and cluttering. | Assists individuals in achieving smoother and more fluent speech patterns. |
Interactive Games | Utilizes fun and engaging activities to promote speech development. | Incorporates games and interactive tools to make therapy enjoyable for children and adults. |
Accent Modification | Helps individuals modify or reduce regional or foreign accents. | Focuses on accent modification, allowing individuals to adapt their speech to different settings. |
Group Therapy | Involves therapy sessions with multiple participants. | Offers a supportive group environment for practicing communication skills. |
Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) | Implements tools like communication boards or devices for non-verbal individuals. | Incorporates AAC strategies to aid communication for individuals with speech challenges. |
Oral Motor Exercises | Targets the muscles involved in speech production. | Engages in exercises to strengthen oral muscles for improved speech clarity. |
Breathing Techniques | Focuses on proper breathing patterns for speech support. | Teaches individuals how to control breath to enhance speech fluency and resonance. |
Relaxation Strategies | Aims to reduce speech-related anxiety and tension. | Helps individuals relax during communication, leading to more natural speech. |
Role-Playing | Encourages individuals to practice communication in various scenarios. | Utilizes role-playing to build confidence and adaptability in social interactions. |
It’s important to note that while Direct and Indirect Speech Therapy may differ in their delivery methods, both approaches share the common goal of helping individuals improve their communication skills and overcome speech challenges. The choice of technique depends on the individual’s needs, preferences, and the expertise of the speech therapist.
3. Individualized Education Plan (IEP)
An IEP is a customized plan created for students with disabilities, including speech and language disorders, to outline specific educational goals and accommodations to help them succeed in the classroom.
Advantages of Individualized Education Plan (IEP)
Speech therapy IEPs offer several benefits:
- Personalized Intervention: IEPs allow speech therapists to develop personalized intervention plans, ensuring that the student’s speech needs are adequately addressed.
- Targeted Progress Tracking: With measurable goals and regular progress monitoring, IEPs enable speech therapists to track the student’s progress accurately and make data-driven decisions.
- Enhanced Communication Skills: By focusing on specific communication goals, IEPs help students improve their speech and language skills, leading to better communication in daily life.
- Increased Confidence: As students achieve their speech therapy goals, their confidence in communication grows, positively impacting their academic and social interactions.
- Involvement of Parents and Educators: The success of a speech therapy IEP depends on the collaboration between speech therapists, parents, and educators. Regular communication and updates ensure that everyone is informed about the student’s progress and can provide consistent support.
Disadvantages of Individualized Education Plan (IEP)
- Time Constraints: Limited therapy time may make it challenging to address all communication goals fully. Speech therapists must prioritize goals based on the student’s most pressing needs.
- Generalization of Skills: Transferring speech and language skills from therapy sessions to real-life situations can be challenging. Speech therapists work with educators and parents to facilitate generalization.
4. Fluency Shaping Therapy
This therapy focuses on helping individuals who stutter to improve their speech fluency through various techniques, such as controlled breathing, easy onset of speech, and relaxed articulation.
The Fluency Shaping Technique, also known as Fluency Shaping Therapy, is a specialized method used to treat speech disorders, particularly stuttering. This evidence-based approach aims to improve fluency, rhythm, and speech rate, providing individuals with the tools to communicate effectively and confidently.
The Fundamentals of Fluency Shaping Technique
Fluency shaping therapy is based on several foundational principles that form the backbone of this transformative technique. Let’s explore these core concepts:
- Smooth Movement: Striving for smooth and continuous speech patterns forms the basis of the Fluency Shaping Technique. By promoting effortless transitions between sounds and words, individuals can achieve fluency.
- Slowing Speech Rate: Encouraging a controlled and deliberate pace in speech helps individuals gain mastery over their communication. Slower speech facilitates greater precision and fluency.
- Breath Control: Proper breath control plays a crucial role in fluency. The technique emphasizes efficient inhalation and exhalation patterns to support fluent speech.
- Gentle Onsets: Avoiding forceful or abrupt speech starts, and embracing gentle onsets, allows for smoother communication.
- Continuous Phonation: Sustaining phonation during speech allows for fluidity and an uninterrupted flow of words.
- Reduced Articulatory Effort: By minimizing excessive muscular effort during speech, individuals can enhance their fluency.
The Process of Fluency Shaping Technique
To fully grasp the Fluency Shaping Technique, it is essential to understand its step-by-step process. Each stage is carefully designed to build upon the previous one, leading to remarkable improvements in speech fluency.
- Evaluation and Goal Setting: The journey begins with a comprehensive evaluation conducted by a speech-language pathologist. This assessment helps identify individual challenges and sets personalized goals for therapy.
- Establishing the Foundation: During this phase, individuals learn the foundational principles of the Fluency Shaping Technique. Techniques such as light articulatory contacts, slowed speech rate, and continuous phonation are introduced and practiced.
- Controlled Fluency: As therapy progresses, individuals work on achieving controlled fluency in structured environments. Various speech tasks are practiced, emphasizing the principles learned earlier.
- Generalization: The next step focuses on carrying fluency into everyday communication situations. Generalization allows individuals to apply the technique in real-life scenarios.
- Maintenance and Support: In the final phase, therapy transitions into maintenance and support. Individuals continue to practice and refine their fluency skills independently, while occasional sessions with the speech-language pathologist provide ongoing guidance.
Benefits of the Fluency Shaping Technique
The Fluency Shaping Technique offers a multitude of benefits for individuals seeking to enhance their communication abilities and overcome speech challenges.
- Enhanced Communication Skills: Mastering the Fluency Shaping Technique leads to improved communication skills, enabling individuals to express themselves confidently and effectively.
- Increased Confidence: As fluency improves, individuals experience a boost in self-confidence, leading to better social interactions and increased self-esteem.
- Overcoming Stuttering: For individuals facing stuttering challenges, the Fluency Shaping Technique offers a proven method to minimize speech disruptions and improve overall fluency.
- Professional Growth: Improved communication can lead to enhanced career prospects and professional growth.
- Positive Social Impact: Enhanced communication skills positively impact personal relationships and social interactions, fostering meaningful connections with others.
- Stress Reduction: Reduced speech-related anxiety and stress are common outcomes of fluency shaping therapy.
In a nutshell, The Fluency Shaping Technique is a powerful tool that empowers individuals to overcome speech challenges and unlock their true communication potential. Through its systematic approach and evidence-based principles, this transformative technique offers hope, confidence, and improved fluency to individuals of all ages. If you or someone you know faces speech impediments or seeks to enhance communication skills, consider exploring the remarkable world of fluency shaping therapy.
5. Short-term Speech Therapy
Short-term speech therapy typically involves a limited number of sessions, often targeting specific, immediate goals. It may be suitable for clients with minor speech or language difficulties.
Short-term speech therapy is a specialized form of intervention designed to address speech and language disorders efficiently. It targets individuals of all ages who struggle with speech-related difficulties, ranging from stutters and lisps to language comprehension issues.
The Impact of Short-term Speech Therapy
Short-term speech therapy can have a profound impact on individuals facing communication challenges. Whether it’s a child experiencing developmental delays or an adult coping with a post-stroke speech disorder, this therapy offers tailored solutions to foster clear and effective communication.
How Does Short-term Speech Therapy Work?
Short-term speech therapy employs a strategic and comprehensive approach to address various communication disorders. The process involves several stages, including:
- Initial Evaluation and Assessment: The journey begins with a thorough evaluation conducted by certified speech-language pathologists. They assess the individual’s speech patterns, language comprehension, and any underlying factors contributing to the communication difficulty.
- Goal Setting: After the evaluation, specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals are set to target the individual’s unique speech and language challenges effectively.
- Tailored Intervention Plans: Speech therapists design customized intervention plans based on the evaluation results and identified goals. These plans incorporate a range of evidence-based techniques to foster speech and language development.
- Regular Therapy Sessions: The individual participates in regular short-term speech therapy sessions, typically ranging from a few weeks to a few months. These sessions are dynamic, engaging, and adapted to the individual’s progress.
- Progress Monitoring: Throughout the therapy journey, progress is continuously monitored, and the intervention plan is adjusted as needed to ensure optimal results.
The Advantages of Short-term Speech Therapy
The benefits of short-term speech therapy extend far beyond improved communication skills. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
- Enhanced Confidence and Self-Esteem: As communication improves, individuals gain confidence in expressing themselves, leading to increased self-esteem and a more positive self-image.
- Improved Social Skills: Better communication fosters meaningful interactions and allows individuals to form stronger social connections.
- Academic Success: Children who receive short-term speech therapy often experience better academic performance due to improved language skills.
- Professional Growth: For adults, enhanced communication skills can open doors to new career opportunities and professional advancement.
- Stress Reduction: Overcoming communication challenges can significantly reduce stress and frustration, leading to improved overall well-being.
Who Can Benefit from Short-term Speech Therapy?
Short-term speech therapy can be beneficial for a diverse range of individuals facing communication difficulties. Here are some groups that can benefit:
- Children with Speech Disorders: Children experiencing speech disorders such as articulation issues, phonological disorders, or language delays can make remarkable progress with short-term speech therapy.
- Individuals with Aphasia: Aphasia, often resulting from strokes or brain injuries, affects language and communication. Short-term speech therapy can aid in regaining language abilities.
- People with Fluency Disorders: Stuttering and cluttering are examples of fluency disorders that can be effectively addressed through short-term speech therapy.
- Those with Voice Disorders: People with voice disorders, such as vocal nodules or vocal cord paralysis, can benefit from speech therapy to improve their voice quality.
- Individuals with Social Communication Difficulties: Some individuals struggle with social communication, making it challenging to engage in conversations. Short-term speech therapy can help them develop appropriate communication skills.
In a nutshell, Short-term speech therapy is a powerful tool in transforming communication abilities swiftly and effectively. Whether it’s addressing speech disorders in children, helping adults recover from aphasia, or aiding individuals in achieving clear and confident communication, this therapy can create life-changing results. With a tailored intervention plan, the guidance of skilled speech-language pathologists, and dedication, the journey towards improved communication becomes an empowering and rewarding experience.
So, if you or someone you know is struggling with speech and language challenges, don’t hesitate to explore the wonders of short-term speech therapy and unlock the doors to effective and confident communication.
6. Long-term Speech Therapy
Long-term speech therapy is a more extended and comprehensive approach that continues over an extended period. It’s suitable for clients with more complex or severe communication challenges.
Long-term speech therapy offers a transformative journey towards improved communication skills and enhanced quality of life. Through personalized treatment plans, innovative techniques, and the unwavering support of therapists and families, individuals can overcome speech challenges and thrive in their interactions with the world. Whether it’s a child taking their first steps towards clear speech or an adult regaining communication after an injury, long-term speech therapy empowers individuals to express themselves with confidence for a lifetime.
Tailored Treatment Plans for Individuals
Every individual is unique, and so are their speech therapy needs. Long-term speech therapy offers personalized treatment plans that cater to each person’s specific challenges and goals. Therapists assess speech and language abilities and design individualized plans to target areas that require improvement. This tailored approach ensures efficient progress and a higher likelihood of success.
Techniques in Long-term Speech Therapy
- Articulation Therapy: This technique focuses on helping individuals produce speech sounds correctly. It involves exercises and drills to improve the clarity of speech and enhance overall articulation.
- Language Intervention: Language delays and disorders are addressed through language intervention, where therapists use various strategies to enhance vocabulary, grammar, and comprehension skills.
- Fluency Techniques: For individuals experiencing stuttering or fluency issues, fluency techniques are employed to improve the flow and rhythm of speech.
- Voice Therapy: Voice disorders are tackled through voice therapy, which involves exercises to strengthen the vocal cords and improve vocal quality.
7. Cognitive Therapy
Cognitive therapy in speech therapy focuses on improving language processing, memory, attention, problem-solving, and other cognitive skills that are essential for communication. Cognitive therapy in speech therapy is a specialized approach that focuses on improving communication skills by targeting cognitive processes. Unlike traditional speech therapy that concentrates solely on articulation and pronunciation, cognitive therapy delves deeper into the underlying cognitive functions related to language production and comprehension. By addressing these cognitive aspects, individuals can overcome communication barriers more effectively and gain confidence in their verbal expression.
The Connection Between Cognitive Functions and Speech
Before diving into the techniques and benefits of cognitive therapy in speech therapy, it’s essential to understand the intricate connection between cognitive functions and speech. Several cognitive processes play a vital role in successful communication:
- Attention and Focus: The ability to concentrate on verbal stimuli and maintain attention during conversations is crucial for effective communication.
- Memory and Recall: Memory plays a significant role in language production, as individuals need to recall words, phrases, and grammar rules in real-time.
- Problem-Solving: Communication often involves quick thinking and problem-solving, especially in fast-paced conversations or when encountering unfamiliar words or situations.
- Executive Functions: Planning and organizing thoughts before speaking, inhibiting irrelevant information, and switching between topics are essential executive functions for clear communication.
Techniques Used in Cognitive Therapy for Speech
Cognitive therapy in speech therapy employs a range of effective techniques designed to enhance cognitive functions and, consequently, communication skills. Some of these techniques include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is widely used in cognitive therapy for speech disorders. It helps individuals identify negative thought patterns related to their communication difficulties and replace them with positive and constructive thinking. This approach not only improves communication but also boosts self-esteem.
- Metacognitive Training
Metacognitive training focuses on helping individuals become aware of their cognitive processes during communication. By understanding how they think and apply strategies for better expression, individuals can refine their communication abilities.
- Mindfulness Practices
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and breathing exercises, can significantly reduce anxiety and stress related to communication challenges. This relaxed state of mind enhances speech fluency and overall communication.
- Problem-Solving Strategies
Teaching problem-solving strategies equips individuals to handle communication obstacles effectively. By learning how to approach difficult situations, they can communicate with more ease and confidence.
Benefits of Cognitive Therapy in Speech Therapy
Cognitive therapy in speech therapy offers a plethora of benefits that positively impact individuals’ lives and their ability to interact with others effectively. Some of these advantages include:
- Improved Communication Skills
The primary benefit of cognitive therapy is a significant improvement in communication skills. Individuals learn how to articulate their thoughts more clearly, overcome speech obstacles, and engage in meaningful conversations.
- Enhanced Confidence
As communication skills improve, so does an individual’s confidence. They feel more comfortable expressing themselves, which can lead to increased social interactions and a higher quality of life.
- Reduced Social Isolation
Individuals with speech disorders often experience social isolation due to communication difficulties. Cognitive therapy helps break down these barriers, fostering connections with others and reducing feelings of loneliness.
- Academic and Professional Advancement
Effective communication is crucial for academic and professional success. Cognitive therapy equips individuals with the skills needed to excel in their studies and careers.
In a nutshell, targeting cognitive processes, this innovative therapy unlocks new possibilities for clear and effective communication. With improved communication skills, individuals gain confidence, build connections, and thrive in both personal and professional aspects of life. If you or someone you know is facing speech-related difficulties, consider exploring the benefits of cognitive therapy to embark on a journey of enhanced communication and self-expression.
8. Contextual Therapy
Contextual therapy considers the environmental and social factors that affect communication. It emphasizes improving communication skills within the context of the client’s daily life.
Contextual Therapy is an evidence-based approach used by speech therapists to address various speech and communication disorders. It focuses on the individual’s unique linguistic and cultural context, tailoring therapy to suit their specific needs. By considering the person’s surroundings, relationships, and daily experiences, therapists can develop a more personalized and effective treatment plan.
Key Principles of Contextual Therapy
To fully grasp the essence of Contextual Therapy, it is essential to understand its core principles:
- Cultural Competence: Emphasizing cultural sensitivity and understanding the influence of cultural backgrounds on communication.
- Holistic Approach: Addressing the person as a whole, considering emotional, social, and cognitive factors alongside speech challenges.
- Collaboration: Encouraging active involvement of the individual’s support network, such as family and friends, in the therapy process.
- Functional Communication: Focusing on real-life situations and improving communication abilities in practical contexts.
- Client-Centered Therapy: Tailoring treatment plans to meet the individual’s unique goals and aspirations.
Contextual Therapy Techniques and Strategies
- Narrative Therapy: Using storytelling to explore emotions, thoughts, and experiences, helping individuals express themselves more fluently.
- Group Therapy: Encouraging communication in a group setting, allowing individuals to learn from each other and build social skills.
- Video Modeling: Utilizing video examples to demonstrate effective communication behaviors and encourage imitation.
- Journaling: Keeping a personal journal to reflect on daily experiences and emotions, promoting self-expression.
- Role-Playing: Practicing communication in simulated scenarios to boost confidence in real-life situations.
Benefits of Contextual Therapy in Speech Therapy
Contextual Therapy offers several advantages over traditional speech therapy approaches:
- Enhanced Communication Skills: By focusing on practical communication, individuals develop skills they can apply in everyday life.
- Improved Confidence: The personalized nature of Contextual Therapy boosts self-esteem and confidence in individuals.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Acknowledging cultural diversity ensures that therapy is respectful and inclusive.
- Stronger Support System: Involving family and friends in therapy creates a robust support network for the individual.
- Long-Term Results: Contextual Therapy aims to build lasting communication abilities that extend beyond therapy sessions.
Example Case: Anna’s Journey to Confident Communication
Background: Anna, a 9-year-old girl, has been struggling with a stuttering disorder since early childhood. This condition has affected her self-esteem, leading to social anxiety and difficulties in forming friendships.
Contextual Therapy Approach
- Cultural Understanding: Anna’s speech therapist, Dr. Rodriguez, takes the time to learn about Anna’s cultural background and family dynamics. This understanding helps in creating a comfortable and supportive therapy environment.
- Holistic Assessment: Dr. Rodriguez conducts a comprehensive evaluation, considering Anna’s emotional well-being, academic performance, and social interactions alongside her speech challenges.
- Involving Family: Dr. Rodriguez actively involves Anna’s parents in the therapy process. They learn strategies to support Anna’s speech development at home and in everyday situations.
- Real-Life Practice: Rather than focusing solely on fluency exercises, Dr. Rodriguez incorporates role-playing and real-life scenarios into the therapy sessions to enhance Anna’s functional communication skills.
- Setting Goals with Anna: Dr. Rodriguez discusses Anna’s personal goals and interests, aligning therapy objectives with her aspirations.
Results: Over time, Anna’s confidence grows, and her stuttering reduces significantly. With continuous support from her therapist and family, she develops effective communication strategies and forms meaningful connections with her peers.
9. Family Therapy
Family therapy involves the family members in the therapeutic process to support and enhance the communication skills of the individual with speech difficulties. It helps create a supportive environment for the client’s progress.
The Role of Family in Speech Therapy
Family plays a pivotal role in an individual’s communication development. From the early stages of language acquisition to refining communication skills, family members are influential in shaping an individual’s ability to express thoughts and emotions effectively. Involving the family in speech therapy sessions creates a supportive and nurturing environment that fosters progress and strengthens family connections.
Benefits of Integrating Family Therapy in Speech Therapy
- Holistic Approach: By incorporating Family Therapy, speech therapists can adopt a holistic approach that considers not only the individual’s speech challenges but also the family’s communication patterns and dynamics.
- Increased Motivation: Family involvement boosts the individual’s motivation and commitment to speech therapy exercises and activities.
- Consistency in Practice: Family members can reinforce speech exercises and language activities at home, promoting consistent practice and improvement.
- Improved Generalization: Skills learned in speech therapy sessions can be better generalized into real-life situations where family members actively support and encourage the individual.
- Enhanced Communication Strategies: Family Therapy equips family members with effective communication strategies, enabling them to interact more constructively with the individual receiving speech therapy.
- Emotional Support: Family involvement provides emotional support and encouragement during the speech therapy journey, reducing anxiety and promoting confidence.
Family-Centered Speech Therapy Techniques
- Communication Modeling: In Family-Centered Speech Therapy, therapists demonstrate effective communication techniques to family members, encouraging them to mirror these techniques when interacting with the individual.
- Language-Rich Environment: Speech therapists guide families in creating a language-rich environment at home, incorporating language-building activities into daily routines.
- Collaborative Goal Setting: The family, alongside the speech therapist, collaboratively sets communication goals tailored to the individual’s needs and preferences.
- Positive Reinforcement: Family members are encouraged to provide positive reinforcement and praise for the individual’s speech progress and efforts.
- Reading and Storytelling: Reading books and engaging in storytelling sessions as a family enhances language development and listening skills.
- Game-Based Therapy: Involving the family in game-based speech therapy activities fosters enjoyment and engagement while honing communication skills.
10. Recreational Therapy
While not specific to speech therapy, recreational therapy can complement speech therapy by using recreational activities to promote communication skills, social interaction, and overall well-being.
- Therapeutic Recreation
- Recreational Activities for Therapy
- Holistic Development through Recreation
- Recreational Therapy Benefits Speech
References:
- Treatment Resource Manual for speech-language pathology 5th edition Froma P. Roth, colleen K. wor [Book]
- Clinical Methods and Practicum in Speech-Language Pathology M. N. Hegde, Ph. D.Deborah Davis, M.A [Book]
- Assessment in Speech-Language Pathology A Resource Manual 5th Edition, Kenneth G. Shipley, Julie G. McAfee [Book]
- Introduction to communication sciences and disorders – Gary Weismer, David K. Brown [Book]
- The Speech-Language Pathology Treatment Planner – Keith Landis [Book]
You are reading about:
Types of Speech Therapy – Individual and Group Therapy






0 Comments